FORTUNE’s 2023 Change the World list is being led this year by a group of companies that are leading the EV revolution – converting cars and trucks from internal combustion to electricity – in one of the world’s most important net-zero missions. The four companies leading the push to convert the world’s most car-happy nation to electric vehicles, all in the #1 spot are: Tesla, General Motors, South Korea’s SK On which develops batteries for EV cars, and ChargePoint, operators of a network of 240,000 charging locations across the U.S.. Continue reading
Tag Archives: Electric vehicles
EV Charge Anxiety: 67 percent of UK EV drivers prepared to pay to reserve a charging bay
The lack of availability and accessibility of current EV charge points, coupled with damaged infrastructure, incompatibility and inadequate payment options is causing frustration amongst UK EV drivers. As a result, over two-thirds (67 percent) of respondents are prepared to pay a premium to reserve a public charging bay to ensure they can power up their vehicles. Just over a quarter (27 percent) are willing to part with up to £10, and 33 percent up to £5. A further 7 percent would even be prepared to go higher at over £10, all to avoid ‘charge anxiety’. Continue reading
Transforming Urban Mobility: Toward a Smarter, Greener, and Safer Future
At this year’s MicroMobility Europe (MME) in Amsterdam, Segway pleased to unveil the groundbreaking innovations that shape our vision for a better way to navigate our cities. In an era where technology is reshaping the way we move, Segway proudly introduces Segway Pilot Edge—an extraordinary AI module that seamlessly integrates with multiple e-scooter models. This revolutionary innovation places rider safety at the forefront by providing real-time insights and predictive analytics. With Segway Pilot Edge, we empower micromobility operators to optimize fleet management and operational efficiency, making micromobility smarter than ever before. Continue reading
EV Chargers: How many do we need?
Supporters of vehicle electrification point to the more than 140,000 EV charging stations currently deployed across the United States – including Level 2 AC and Level 3 DC fast chargers and both public and restricted access units – as a sign that a budding system to support our transportation transformation is in place. Continue reading
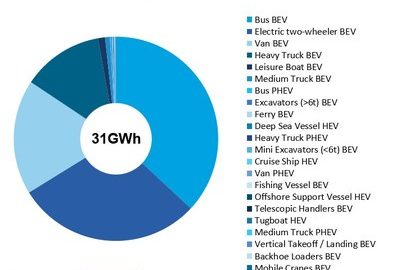
30 Giga-Watt Hours of Electric Vehicle Markets Beyond Cars, Reports IDTechEx
Electric vehicle markets are growing globally – in total IDTechEx’s latest master electric vehicle report “Electric Vehicles: Land, Sea & Air 2022-2042” finds 35.7 million electric vehicles (EV) were sold in 2021 and predicts this will rise to over 74 million by 2030. Continue reading
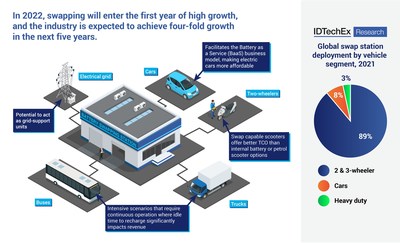
Battery Swapping: From Two-Wheelers to Trucks, Reports IDTechEx
The conductive fast-charging system as we know it today has drawbacks such as long dwell times, high power demand from the grid, availability and reliability issues, and the need for end-users to deal with heavy cables, dirty connectors, and buggy user interfaces. Battery-swapping is an emerging technology that aims to address all of these shortcomings. Besides easily upgrading battery technology, reducing the purchase price of EVs (by decoupling the cost of the battery from the EV), and massively decreasing charging times, it is also important to note that the battery swapping stations themselves can become independent energy storage facilities with grid-balancing ability. As we electrify the various vehicle segments, can battery swapping be considered a viable recharging strategy for them all? Continue reading
L-Charge plans to accelerate the deployment of EV Charging Infrastructure in Europe
While Norway, the Netherlands and Germany are leading the race on electrification and infrastructure provision with a planned ratio of 3 EVs per public charge point, many European countries are lagging behind. In contrast, there are currently 22 EVs per public charge point in Ireland, and 27.2 EVs per public charge point in the UK. Increasing the number of grid-tied chargers is often a difficult, lengthy and cost onerous process because of grid constraints and aging infrastructure. Continue reading